Radio Systems of Soviet/Russian manned
spacecraft
Sven Grahn
Vostok
The list below is a
compilation
of frequency information from various sources.
Shortwave AM voice:
9.019 MHz downlink,
uplink on 10.012
MHz
(Vostok
1). Power: 6-10 watts
20.006 MHz downlink, uplink on
22.205 MHz
15.765 MHz (AM voice?,
Vostok 2)
VHF FM
voice
143.625 MHz downlink for "Zarya" FM voice
system.
139.208 MHz uplink for
"Zarya".
"Signal" telemetry beacon
19.948 MHz "Signal"
simple biomedical telemetry beacon (Vostok 5)
19.990 MHz "Signal"
simple biomedical telemetry beacon (Vostok 4)
19.995 MHz "Signal"
simple biomedical telemetry beacon (Vostok 2,
3, 6)
"High-speed" telemetry
66,71,76 MHz "Tral-P1-1" and
"Tral-P1-2"
telemetry systems
Television system
83 MHz "Seliger-Tral-D" TV system. Developed by OKB
MEI, A F Bogomolov
Radar
transponder
2790-2820 MHz "Binokl" radar
transponder.
Unkown purpose and
characteristics
183 MHz, maybe lasts tage of the
launcher?
Recovery
beacon
10.003 MHz Recovery beacon transmitter P-37. Antenna
deployes after opening of parachutre. "Peleng" in table
below.
Command link
47.9 to 49.0 MHz MRV-VS
Where are the
antennas
for these frequencies located?
The sketch below is of
Soviet
origin and has been in my files for more than ten years. I do not know
where it comes from, but the translated caption is reproduced to the
right
of the picture.
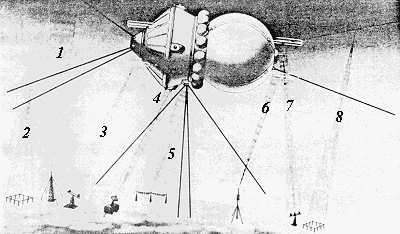 |
- Transmission
of
operational
telemetry from onboard the spacecraft ("Signal")
- Reception of
terrestrial broadcasting
stations
- Transmission
of
telemetry and
television images from onboard the spacecraft
- Measurement
of
the orbit of
the spacecraft
- Two-way
telephony and telegraphy
shortwave communications
- Command
reception
- Two-way VHF
telephony
- Transmission
of
operational
telemetry and telegraphy information during the landing phase ("Signal")
|
Here is a brief interpretation of this
figure
and table:
- This is the
keyed-CW
signal
on 19.995 MHz.
- Remember, there
was a
car-radio
dial in the Vostok cabin.
- These are the four
"fat" antennas
at the back of the service module. Each of these antennas are about a
meter
long, which, if a quarter-wavelenth, indicates 4 meters or about 75 MHz
frequency. The antennas are "fat" giving them broadband
characteristics.
In this way they could cover the 83 MHz TV frequency and
possibly
other frequencies. It is possible that the TV transmitter also carried
telemetry, but I think that there were separate telemetry transmitters,
probably in the 61-76 MHz band.
- This is the
"Binokl"
radar transponder
system working on 2700-2800 MHz. I think that the "Binokl"
antennas
are the little white discs and that the "Irtysh" inteferometer antennas
are the little loop straddling the white disc. The "Irtysh" system is
supposed
to work in the decimeter-wave band. Let me guess that the frequency is
around 1 GHz.
- This is the 20.006
MHz
AM voice (and 9.019, 15.765 MHz) link.
- This are the
"trombone" antennas
on top of the re-entry vehicle. The frequency is low, probably below
100
MHz.
Command reception at 47.9-49.0 MHz probably.
- This is the little
VHF
dipole
on top of the re.entry vehicle. It is for 143.625 MHz.
- This is the 19.995
MHz
simple keyed-CW telemetry. These antennas are monuted directly on the
re-enrty
vehicle and not on the straps hold the re-entry vehicle to the service
module. In this way, the would work all the way until the re-entry heat
burned them away. But, was the cosmonaut competetly out of voice contat
once the service module had been released?
Specific radio systems in
early
Soviet satellites:
| Spacecraft |
Radar
|
Interferometer
|
Telemetry
|
TV
|
Voice
|
Orbital
beacon
|
Recovery
beacon
|
| Sputnik 1 |
"Binokl" in
R-71
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Sputnik
2 |
"Binokl" in
R-71
|
- |
"Tral-D"
biomed1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Sputnik 3 |
"Binokl-D"1
|
"Irtysh-D"1
|
"Tral-D"1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Vostok |
"Binokl-D"1
"Rubin"2
|
"Irtysh-D"1
|
"Tral-P1"2 |
"Seliger-Tral-D"1
"Topaz"2 |
"Zarya"1 |
"Signal"1 |
"Peleng"1 |
1 = "Roads to
Space"
2 = "Energia
1946-1996"
Voskhod
10.003 MHz
Recovery beacon
transmiter P-37. Antenna deployes after opening of parachute. "Peleng"
in table above.
17.365 MHz AM voice
18.035 MHz AM voice
(listen to R.S. Flagg's recording
of
Komarov's [Rubin] call to ground station Vjezna 2)
19.9944 MHz "Signal"
simple biomedical telemetry beacon (Voskhod 1)
19.996 MHz "Signal"
simple biomedical telemetry beacon (Voskhod 2)
143.625 MHz "Zarya"
FM voice system
Early
Soyuz (7K-OK)
15.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
18.035 MHz AM voice?
18.060 MHz AM voice?
20.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
121.75 MHz was the
main FM voice downlink
922.75 MHz
Soyuz
Ferry
(7K-T)
18.060 MHz
20.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
121.75 MHz was the
main FM voice downlink
166.0 MHz PPM-AM
telemetry
922.75 MHz
925.24 MHz
926.06 MHz
Soyuz
for
ASTP (7K-TM)
18.060 MHz
20.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
121.75 MHz was the
main FM voice downlink
142.417 MHz
secondary
FM voice downlink
192.0 MHz PCM/FM
telemetry
296.8 MHz
Apollo-compatible
AM voice link.
463 MHz used for
downlinking TV. A frequency-modulated link. The system was called
Krechet,
developed by VNII-30, A F Polushkin.
919.76 MHz
2870 MHz
2900 MHz
Soyuz
S (7K-S)
20.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
166.0 MHz PPM-AM
telemetry
Soyuz
T
(7K-ST)
20.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
121.75 MHz was the
main FM voice downlink
166.0 MHz PCM/FM
telemetry
922.75 MHz
Soyuz
TM
(7K-STM)
Transmit
121.75 MHz is the
main FM voice downlink
166.0 MHz PCM/FM
telemetry
922.75 MHz
926.05 MHz
Receive
130.167 MHz is the
main FM voice uplink
768.96 MHz is the
command uplink
Salyut
1
Downlinks
15.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
922.754 MHz
Salyut
2
See Salyut 3
Kosmos
557
Downlinks
15.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
20.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
922.75 MHz
Salyut
3
Downlinks
19.944 MHz FSK-PDM
telemetry
143.625 MHz was the
main FM voice downlink
180 MHz PPM-AM
telemetry
Salyut
4
Downlinks
15.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
20.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
121.75 MHz was the
main FM voice downlink
192 MHz PPM-AM
telemetry
922.75 MHz
925.24 MHz
926.06 MHz
Salyut
5
Downlinks
19.944 MHz FSK-PDM
telemetry
19.992 MHz FSK-PDM
telemetry
143.625 MHz was the
main FM voice downlink
180.0 MHz PPM-AM
telemetry
Salyut
6
Downlinks
15.009 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
20.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
121.75 MHz was the
main FM voice downlink
192.0 MHz PPM-AM
telemetry
922.75 MHz
925.24 MHz
926.06 MHz
2802 MHz
Salyut
7
Downlinks
15.009 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
20.008 MHz CW-PDM
telemetry
142.417 MHz was the
main FM voice downlink
165 MHz PPM-AM
telemetry
(initially the frequency was 166.0 MHz)
192 MHz PPM-AM
telemetry
922.75 MHz
925.3 MHz
926.07 MHz
Mir
Downlinks
Frequency
(MHZ) |
Use |
|
|
| 121.75 |
A back-up FM
voice link |
| 130.167 |
An FM voice link
used during
EVA. Also used to transmit TORU commands to Progress. |
| 143.625 |
The main FM
voice downlink |
| 166.0 |
The PCM/FM
telemetry channel (BR9-TsU system) |
| 463 |
Used for
downlinking TV.
It is a frequency-modulated link |
| 636.0 |
Used for PCM/FM
telemetry very similar to the 166 MHz channel (BITS TM
system) |
| 638.0 |
Used for PCM/FM
telemetry very similar to the 166 MHz channel (BITS TM
system) |
| 922.76 |
Contains
telemetry and other
signals on subcarriers. Russian name: KVANT. The primary use
of
the system is for orbit determination and command
verification.
It has the capability to provide TM and downlink voice but it is not
used
for that normally. |
| 2860 |
The radar
transponder return
channel |

Mir
telemetry
antenna for 630-640 MHz band
Uplinks
768.96 MHz is the
command uplink
121.75 MHz can be
used as a receive frequency also including receiving TORU signals from
Progress
139.208 MHz used
as a receive frequency during Shuttle dockings
2725 MHz is the
radar
transponder Rx frequency
Zarya
- ISS
Control Module (formerly known as FGB)
Transmit
130.167 MHz TORU
transmit to Progress and to Orlan space suit.
632 MHz Used for
PCM/FM
telemetry very similar to the 166 MHz channel on Soyuz. (BR-9TsU-8)
634 MHz Used for
PCM/FM
telemetry very similar to the 166 MHz channel on
Soyuz. (BR-9TsU-8)
2365-2375 MHz Command verification downlink of the
Komparus system (According to Metrolog.ru
web site)
Receive
121.125 MHz Voice
from Orlan space suit.
121.75 MHz receive
TORU signals from Progress and from Orlan space suit.
7190-7210 MHz Command link of the Komparus system
(According Metrolog.ru
web site)
See picture
of two "comb" antennas on Zarya scale model.
Zvezda
-
ISS Service Module
Transmit
| Frequency
(MHZ) |
Use |
|
|
| 121.75 |
A back-up FM
voice link
(3.5 W). TORU transmit to Zarya. |
| 130.167 |
An FM voice link
used during
EVA(3.5 W) and in the VHF 2 mode. Also used to transmit TORU commands
to
Progress and to Orlan space suit.. |
| 143.625 |
The main FM
voice downlink
(3.5 W) (VHF 1) |
| 463 |
Used for
downlinking TV.
It is a frequency-modulated link.(15 Watts). Deviation is 10 MHz. |
| 628.0 |
Used for PCM/FM
telemetry very similar to the 166 MHz channel (BITS TM
system,
(BR-9TsU-8)) |
| 630.0 |
Used for PCM/FM
telemetry very similar to the 166 MHz channel (BITS TM
system,
(BR-9TsU-8)) |
| 922-928 |
Contains
telemetry and other
signals on subcarriers. Russian name: REGUL. The primary use
of
the system is for orbit determination and command
verification.
It has the capability to provide TM and downlink voice but it is not
used
for that normally. |
| 2860 |
The radar
transponder return
channel (210 W) |
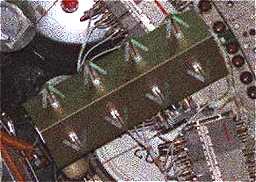
This extract from a
NASA
picture of the Zvezda rear end probably shiows the crossed dipole array
of the REGUL radio system designed to work through a relay satellite.
|
Receive
| Frequency
(MHZ) |
Use |
| 121.125 |
Voice from Orlan
space suit. |
| 121.75 |
Alternate
receive frequency
(VHF 2). Also used to receive TORU signals from Progress and voice from
Orlan
space suit. |
| 139.208 |
Used as a
receive frequency
from the ground (VHF 1). |
| 130.167 |
Used to receive TORU
signals from Zarya |
231
|
Receive telemetry from Orlan space suit
|
| 247 |
Receive telemetry
from Orlan space suit
|
| 420 |
TV receive |
| 463 |
TV receive from
Soyuz, Progress
and ground. |
| 768-774 |
The command
uplink |
| 2725 |
The radar
transponder Rx
frequency |
| 3294 |
Kurs receive |
| 3300 |
Kurs receive |

 [Sven's
Space Place]
[Sven's
Space Place]
 [Space
Radio Notes]
[Space
Radio Notes]

Copyright ©
1996
Sven Grahn


